Referral criteria for ovarian cancer - genetic counselling and genetic testing (in genetics services or in gynaecology oncology multidisciplinary services)
Criteria for genetic counselling and genetic testing (in genetics services or in gynaecology oncology multidisciplinary services)
Family history of ovarian cancer
- recommendations are for anyone who has a risk of having a pathogenic variant (refers to the presence of a pathogenic variant or 'likely pathogenic variant' (which is a variant with strong evidence that suggests it is associated with an increased risk of ovarian cancer) associated with ovarian cancer
- includes women, men, trans people and non-binary people.
Genetics services should offer genetic counselling and genetic testing to anyone who:
- has not had ovarian cancer and
- has a raised probability of having a pathogenic variant (see table on genetic testing criteria below) based on a verified family history and
- has a relative who has had a confirmed diagnosis of breast cancer or ovarian cancer but genetic testing of the relative (or the tissue) is not possible or clinically appropriate (for example, consent is declined)
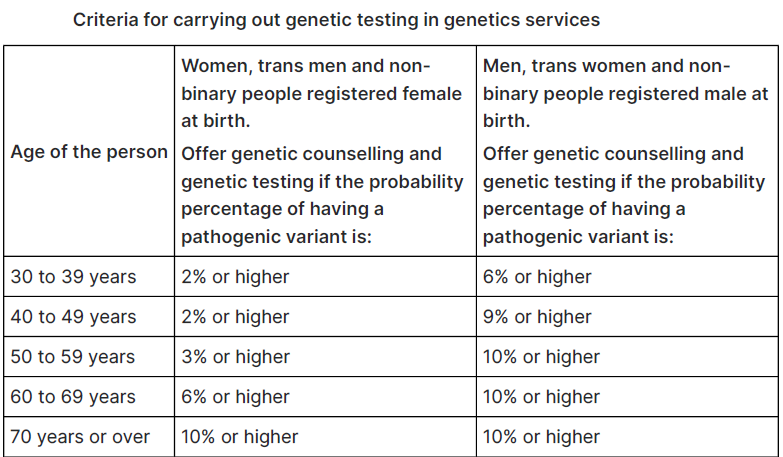
If a person has not had ovarian cancer, genetics services should offer genetic counselling and genetic testing if they are a first-degree relative of a person with a known pathogenic variant (cascade testing).
If a person has not had ovarian cancer, genetics services should offer genetic counselling and genetic testing if:
- they are a second-degree or more distant blood relative of a person with a known pathogenic variant and
- testing of an intervening blood relative is impossible or not clinically appropriate (for example, consent is declined).
If a person has a personal or family history of breast cancer, also see the NICE guideline on familial breast cancer, in particular the sections on the clinical significance of a family history of breast cancer, and referral to a specialist genetic clinic.
With respect to at-risk populations
- recommendation is for anyone who has a risk of having a pathogenic variant associated with ovarian cancer. This includes women, men, trans people and non-binary people.
- recognise and raise awareness that people from the following populations (with at least 1 grandparent from the respective population), have a higher risk of having a founder pathogenic variant associated with familial ovarian cancer, so should be offered referral for genetic counselling and genetic testing for this variant, even if the person has no family or personal history of cancer:
- Ashkenazi Jewish
- Sephardi Jewish
- Greenlander
Also see the NHS Jewish BRCA Testing Programme, which offers BRCA testing to people with Jewish ancestry
Reference:
Related pages
Create an account to add page annotations
Add information to this page that would be handy to have on hand during a consultation, such as a web address or phone number. This information will always be displayed when you visit this page